Class 7: Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems
A cell is the smallest unit of life.
Cells of the same type make a tissue.
Different tissues make up an organ.
Different organs work together in organ systems.
Many organ systems make up a living thing – an organism.
Life Processes
All organisms including cells carry out the following life processes.
- Movement - they can move from place to place or move parts of themselves. Sunflower plants slowly track the motion of the sun across the sky during the day and then back during the nighttime.
- Reproduction - they can make more of themselves. Bacteria are single celled unicellular organisms that reproduce by a process called binary fission.
- Sensitivity - they can sense and respond to changes inside and outside their bodies called stimuli around them. Mimosa pudica is a flowering plant of the pea/legume family. The leaves fold inward and droop when touched or shaken, defending themselves from harm, and re-open a few minutes later.
- Growth - they can increase in size. Seeds germinate using warmth, water and oxygen and the leaves photosynthesize with the help of water and minerals from soil, carbon dioxide and sunlight.
- Respiration - they use glucose and oxygen to release energy. Energy is released when glucose and oxygen react in our cells to produce carbon dioxide and water.
- Excretion - they can produce waste and get rid of it. Excretion is the release of waste in the form of urine, sweat and exhalation of carbon dioxide
- Nutrition - they require food for energy, growth and overall health.
For anything to be living, it should be able to carry out all the above life processes.
Human & Plant Organ Systems
•Circulatory system helps transport oxygen and nutrients to all body cells via blood.
•Respiratory (Gas exchange) System helps take in oxygen into our body and remove carbon dioxide.
•Digestive system helps break down large food molecules into smaller nutrients that can be absorbed into blood.
•Urinary system helps to excrete waste and extra water from the blood.
•Nervous system helps respond to stimuli by transmitting electrical impulses along nerves.
•Skeletal system helps provide movement, protection and support.
Roots, stem, leaves work together in the plant water transport system
The water transport system in plants takes water from the ground up to the leaves by capillary action.
Water is always flowing from this organ system as leaves constantly lose water by evaporation (transpiration).
Human & Plant Organs
The following are fundamental organs in the human body.
•The brain is the control center of the nervous system and is located within the skull. Its functions include muscle control and coordination, sensory reception and integration, speech production, memory storage, and processing of thought and emotion.
•The heart is a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions.
•The lungs are two sponge-like, cone-shaped structures that fill most of the chest cavity. Their essential function is to provide oxygen from inhaled air to the bloodstream and to exhale carbon dioxide.
•The liver lies on the right side of the abdominal cavity. Its main function is to process and control the contents of the blood. This involves breaking down fats, producing urea, filtering harmful substances and maintaining a proper level of glucose in the blood.
•The stomach is a muscular, elastic, pear-shaped bag, lying crosswise in the abdominal cavity. Its main purpose is digestion of food through production of gastric juices (including hydrochloric acid) which break down, mix and churn the food into a thin liquid.
•The intestines are located between the stomach and the anus and are divided into two major sections: the small intestine and the large intestine. The function of the small intestine is to absorb most ingested food in the blood. The large intestine is responsible for absorption of water and excretion of solid waste material.
•The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located at the back of the abdominal cavity, one on each side of the spinal column. Their function is to maintain the body’s chemical balance by excreting waste products and excess fluid in the form of urine.
•The bladder is a muscular organ located in the pelvic cavity. It stretches to store urine and contracts to release urine.
- Roots - anchor the plant to the ground and absorb water and minerals from the ground.
- Stem- holds the plant upright and transports water and nutrients from roots to the leaves.
- Leaves - trap sunlight to make food for the plant by the process of photosynthesis.
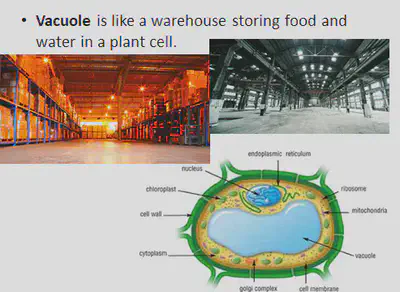
- Plant storage organs e.g. bulbs, storage roots and tubers - store food and water for the plant to use when needed:
Human & Plant Tissues
Tissues contain cells of the same type that perform a certain function.
All organs are made up of tissues. Example: the heart is made up of muscle, nerve, fat and blood tissues.
- Nerve tissue - Made up of nerve cells which transmit electrical messages throughout the body
- Muscle tissue - made up of muscle cells.
- Fat (adipose) tissue - made up of adipose cells. The layer of fat tissue under the skin insulates the body to keep it warm. Pads of fat act as shock absorbers and support and cushion vital organs. The stored fat also provide energy when required.
- Epithelial tissue - made of epithelial cells which form the covering of all body surfaces
Plant Tissue
•Root hair tissue absorb water and minerals
•Xylem tissue transports water up the plant from the roots
•Phloem transports nutrients and food up and down the plant and into storage organs
Specialized Cells
- Red blood cells - carry oxygen.
Special features
- They have a biconcave shape which provides a large surface area for oxygen to pass into them.
- They contain hemoglobin which joins with oxygen.
- They have no nucleus.
- Nerve cells - carry nerve impulses to different parts of the body,
Special features:
- They are long and connected to each other.
- They can carry electrical signals.
3. Ovum (Egg cell) - this is the female reproductive cell which joins with the male reproductive cell by the process of fertilization during sexual reproduction.
Special features:
- It is large
- It carries a food store in the form of yolk .in its cytoplasm
4. Sperm cell - this is the male reproductive cell which joins with the female egg cell by the process of fertilization during sexual reproduction.
Special features:
- It has a long tail for swimming
- It has a head that allows it to enter the female cell.
5. Ciliated epithelial cell - it moves dust particles and germs away from the lungs.
Special features:
- It contains hair-like structures called cilia which waft away the germs and dust particles.
6. Root hair cell - it absorbs water and minerals.
Special features:
- It is long and thin which provides a large surface area for maximum absorption of water and minerals.
7. Palisade cell - absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis and is found in leaves.
Special features:
- Lots of chloroplasts.
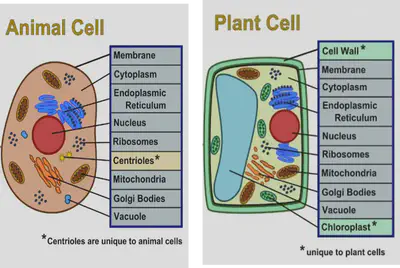
Animal & Plant Cells
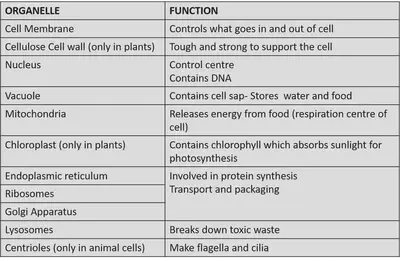
Cell Organelles & their Functions
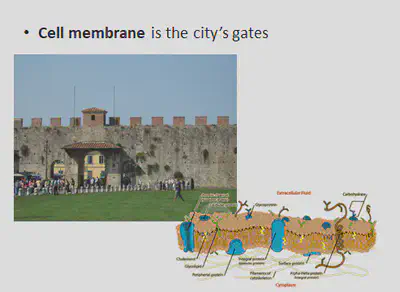
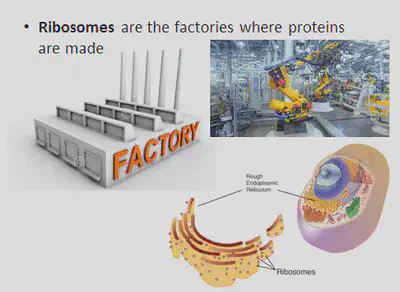
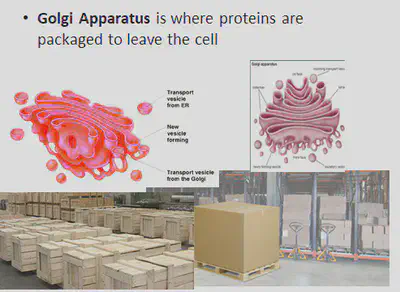
All cell organelles are held in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is a jelly like fluid that holds all the cell organelles and it is where chemical reactions take place.