Class 7: Sound
•Sound is a vibration we can hear.
•A vibrating object makes sound

•Sound travels through air. It travels more quickly through solids than liquids or gases
•Speed of sound in air = 330m/s
•Sound needs particles to travel through them
•Sound cannot travel in a vacuum where there are no particles.
•Sound waves can pass through materials.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ce7AMJdq0Gw
A wave is a vibration or disturbance in space.
Sound waves are longitudinal which means the direction of vibration is parallel to the direction of motion of the wave. Particles in a sound wave experience a back and forth movement.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h90zbDXCW5o
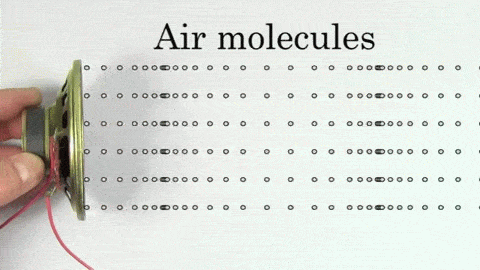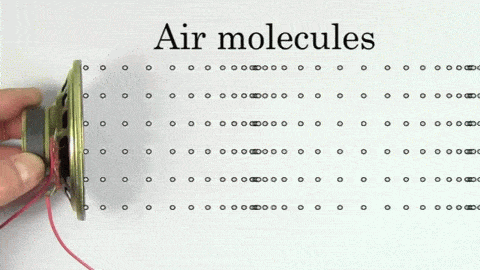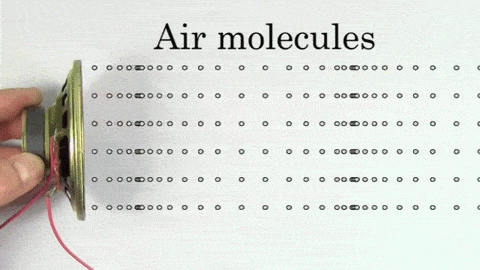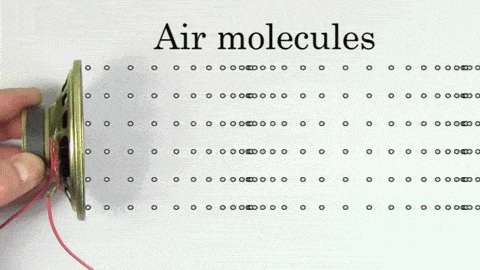
The sound wave contains high pressure areas where particles get closer called compressions and low pressure areas where particles are further away called rarefactions.
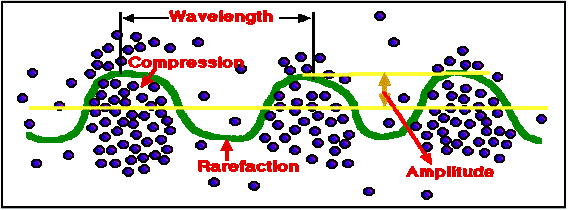
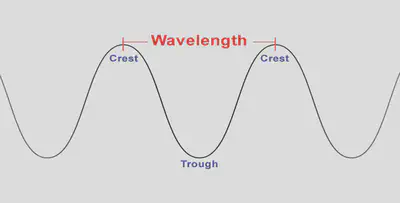
Regions of compressions make the crest of the wave while areas of rarefactions make the trough of the wave. The distance between every two crests or every two troughs is called the wavelength.
Amplitude is the distance that particles move from rest when a sound wave passes through them. The louder the sound the greater the amplitude. The quieter the sound, the shorter the amplitude.

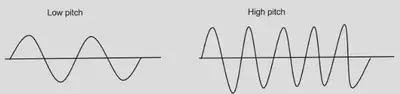
The shorter the wavelength, the higher the pitch of the sound and the higher the frequency.
The longer the wavelength, the lower the pitch of the sound and the lower the frequency.
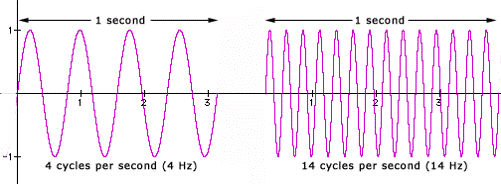
•Frequency is the number of vibrations per second
•Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz)
•1 Hz = 1 Vibration per second = 1 back and forth movement of particles in one second.
Humans can hear frequencies between 20Hz to 20,000Hz.
Sounds below 20Hz are called infrasounds