Class 7: Energy & Changes
Energy from food
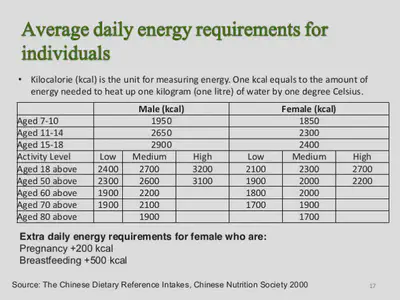
Energy is measured in Joules. We get energy from food. Energy in foods is measured in kiloJoules. It is also measured in kilo Calories. 1 kCal = 4 kJ Different people have different energy requirements per day:
Energy Transfers & Stores
Energy can be stored as:
•Chemical energy in batteries, food and other fuels like petrol/diesel.
•Thermal energy in hot objects
•Kinetic energy in all moving objects
•Elastic potential energy (strain) in objects which are stretched, twisted, bent or compressed (squashed).
•Gravitational potential energy in objects held at high positions.
•Nuclear (atomic) energy inside all materials
Energy can be transferred (moved) from a store of energy) by:
•Forces
•Light
•Electricity
•Sound
•Heating
Law of Conservation Of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can only be transferred from one form to another.
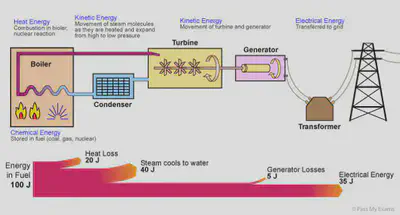
Energy flows
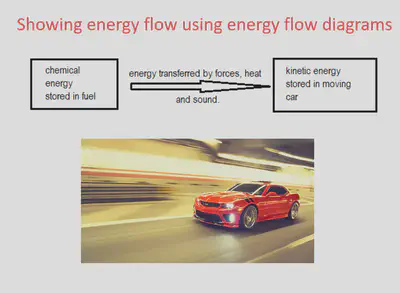
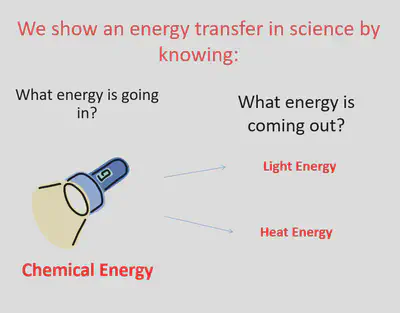
•Since energy is conserved, total energy going into the object equals to the total energy coming out from it.
More examples of energy flows in:
- photovoltaic solar panels - converts light energy into electrical energy
- a greenhouse - converts light energy into t.hermal energy.
- a television - converts electrical energy into light and sound energy.
- an electric heater - converts electrical energy into heat energy
- a car - converts chemical energy into kinetic energy.
- playing a drum - kinetic eneryg into sound energy.
- an explosion - converts chemical energy into kinetic, sound, heat and light energy.
- a torch - converts chemical energy into electrical energy into light energy.
- a star - converts nuclear energy into heat and light energy,
- a battery charger - converts electrical energy into chemical energy.
- a tree - converts light energy into chemical energy.
- a microphone - converts sound energy into electrical energy.
- a nuclear bomb - converts nuclear energy into kinetic, sound, light and heat energy.
- a rocket - converts chemical energy into kinetic energy into gravitational potential energy.
- a glow stick - converts chemical energy into light energy.
- a ball rolling down a slope - converts gravitational potential energy into kinetic energy.
- a generator - converts chemical energy into kinetic energy into electrical energy.
- shooting an arrow from a bow - converts elastic potential energy into kinetic energy.
- a clockwork toy - converts elastic potential energy into kinetic energy.
- a hot air balloon - converts chemical energy into heat energy into gravitational potential energy.
- a light mill - converts light energy into kinetic energy.
- a wind farm - converts kinetic energy into electrical energy.
- a pole vaulter - converts kinetic energy into elastic potential energy into gravitational potential energy.
•Since energy is conserved, total energy going into the system equals to the total energy coming out from it.
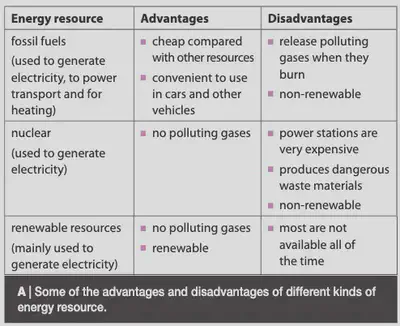
Fuels & Energy resources
•A fuel is a substance that contains a store of chemical or nuclear energy that is transferred into heat and light. A fuel is an energy resource.
•Energy from burning fuels is used to generate electricity in power stations. These fuels have been mainly fossil fuels.
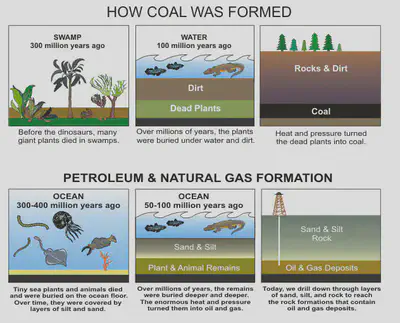
FOSSIL FUELS – Coal, Crude Oil and Natural Gas
These are made over millions of years under heat and pressure from layers of Earth over the remains of organisms. Coal is formed from ferns, plants and trees which hardened due to pressure and heat Oil is formed from smaller organisms, like zooplankton and algae. Intense amounts of pressure caused this complex organic matter to decompose into oil. Natural Gas undergoes the same process as oil; however the process is longer and subject to higher amounts of heat and pressure, causing further decomposition. Fossil fuels are non renewable sources of energy because they cannot be replaced easily once they are used up. It takes millions of years to form them.
Renewable Fuels – can easily be made and replaced once they are used up. The rate at which they are used is less than or equal to the rate at which they are made again.
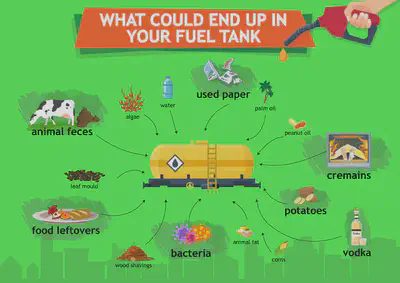
•BIOFUELS – made from plant and animal waste.
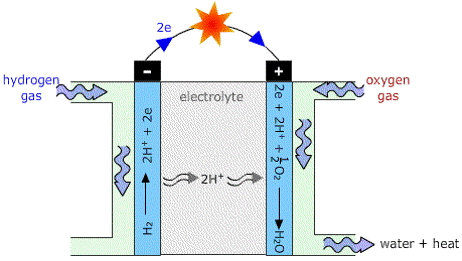
•HYDROGEN GAS – can be made from water. Hydrogen combining with oxygen in fuel cells can produce electricity. Water is the only product which makes hydrogen a clean energy resource.
Other Energy resources
•SOLAR POWER – uses energy from sun to:
a) Heat water – solar panels mounted on roofs are tubes full of water which heats up and can be used to heat the building on provide hot water.

b) Produce electricity –
i)solar cells can convert sunlight energy to electricity directly.

ii)A solar power station focuses sunlight using mirrors onto a tower. The concentrated heat from the sun onto tower heats up water, turns it into steam which can drive turbines to generate electricity.

•WIND TURBINES – use the wind to turn turbines to generate electricity.

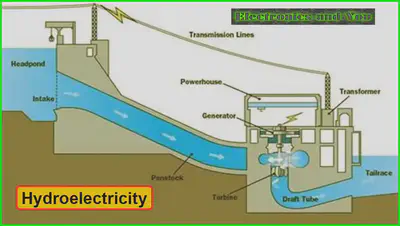
•HYDROELECTRIC POWER – use flowing water to turn turbines and generate electricity. Moving water in waves and tides can also be used.
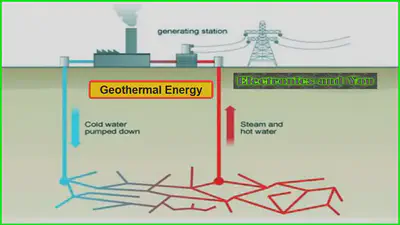
•GEOTHERMAL POWER – use the heat from rocks underground to heat water, turn it to steam to drive turbines and generate electricity.
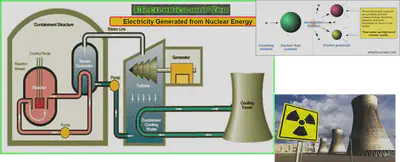
•NUCLEAR ENERGY – uses the energy stored in particles to release heat and light. The heat released can be used to heat water, turn it to steam and drive turbines.
Energy resources depending on the sun
1.Hydroelectricity:
The sun has a store of nuclear energy that is converted to heat and light which we receive on Earth:
To drive the water cycle by using sun’s energy to evaporate water and continue the water cycle (hydroelectric power therefore depends on the sun)
- Fossil fuels
Plants use the sunlight energy to convert it to chemical energy by photosynthesis. The chemical energy gets transferred through food chains. When these plants and animals die and get buried under heat and pressure over millions of years they become fossil fuels.
- Wind & Tidal energy - Energy from the sun also causes wind and waves.
Energy resources that do not depend on the sun:
1. Nuclear fuels
2. Geothermal energy.
How is electricity generated?
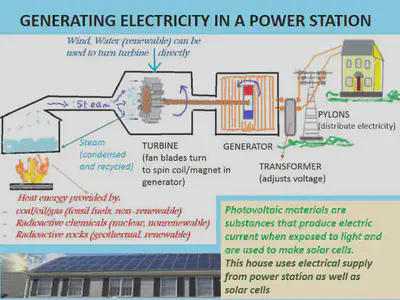
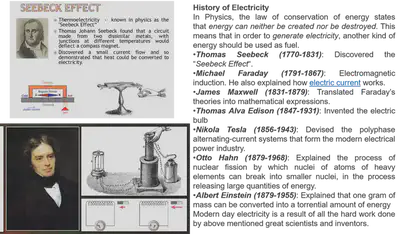
USING RESOURCES
•Renewable energy resources (solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, nuclear, waves and tidal energy) can be regenerated and will never run out but non-renewable energy resources (fossil fuels) are limited and can run out. The rate at which non renewable resources are used up is more than the rate at which they are being formed.
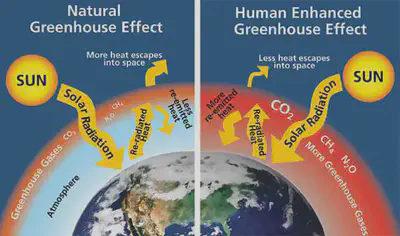
•Burning fossil fuels for energy releases carbon dioxide which is a gas that traps the sun’s heat making the Earth warmer (global warming) leading to climate change.
Energy efficiency
•Not all the energy transferred by a machine is useful. Some of it is wasted.
•The amount of useful energy transferred compared to the total input energy is called the efficiency of a machine.

•An efficient machine has more useful energy transferred than wasted.
•Since an efficient machine wastes less energy and produces more useful energy; it will require less fossil fuel to produce the electricity to run it and so your energy bills will be cheaper.